AI-Driven Self-Organizing Networks (SON) for 5G OPEX Reduction: A Comprehensive Survey and Conceptual Framework
محتوى المقالة الرئيسي
الملخص
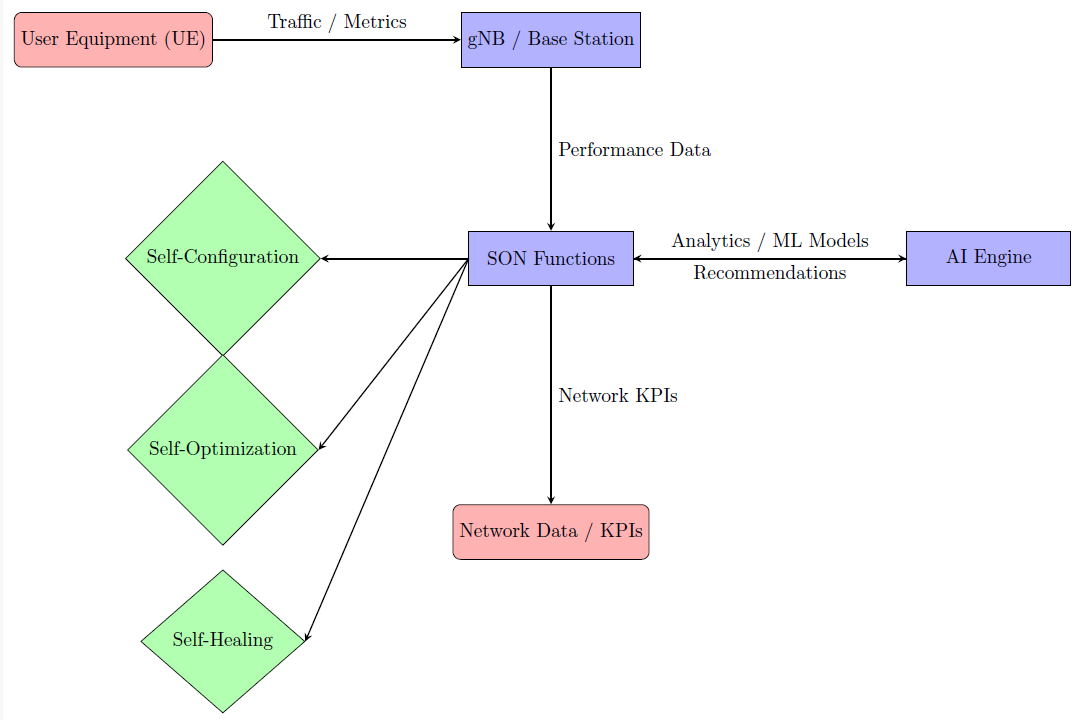
This paper investigates the application of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Self-Organizing Networks (SON) for 5G networks, focusing on coverage enhancement and reduction of Operational Expenditures (OPEX). A conceptual AI-Self Organizing Networks (SON) framework integrated with O RAN architecture is proposed, and an illustrative Python-based simulation is conducted to demonstrate potential trends in coverage probability, energy consumption, and estimated OPEX savings. The simulation results indicate that AI-SON can achieve near-optimal coverage (coverage probability 0.9985) while reducing energy usage and maintenance costs, with an estimated OPEX reduction of 2030% compared to baseline strategies. The study clarifies that the simulation is illustrative and not experimentally validated, providing a foundation for future rigorous evaluations.
التنزيلات
تفاصيل المقالة

هذا العمل مرخص بموجب Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
المراجع
NGMN Alliance, “5G White Paper”, February
3GPP TR 22.864: "Feasibility Study on New
Services and Markets Technology Enablers -
Network Operation; Stage 1 (Release 15)",
September 2016. 16
“lteencyclopedia.” [Online]. Available:
https://sites.google.com/site/lteencyclopedia/ho
me [Accessed: 11-Apr-2022].
D. Warren and C. Dewar, “Understanding 5G:
Perspective on Future Technological
Advancements in Mobile,” GSMA Intell., Dec.
A. Imran, M. A. Imran, A. Abu-Dayya, and R.
Tafazolli, “Self Organization of Tilts in Relay
Enhanced Networks: A Distributed Solution,”
IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun., vol. 13, no. 2, pp.
–779, Feb. 2014.
Ajay R. Mishra “Fundamentals of Network
Planning and Optimisation 2G/3G/4G: Evolution
to 5G”, (2018).
Saad Z. Asif “5G Mobile Communications
Concepts and Technologies”. (2018).
Mobile Network Services. [Online]. Available:
https://getsolupro.com/businessareas/telecommunicationsengineering/services/m
obile-networks-services/ [Accessed: 15-May2022].
K. Horn et al., 'Reinforcement Learning for RAN
Optimization', IEEE Communications Surveys,
Appendices
Appendix A: Simulation Code (Summary)
The simulation used to generate the
illustrative plots is a synthetic Python model.
Key steps: 1. Define user density range (10-200
users/km^2). 2. Model coverage probability
baseline as logistic decline with density. 3.
Model AI-SON improvements by shifting
logistic parameters and adding small gains. 4.
Plot and export figures for inclusion. A
production-grade simulation would replace
synthetic models with stochastic geometry,
path-loss maps, and packet-level simulators
such as ns-3 with 5G m