Enhancing Intrusion Detection System in cloud computing Using Machine Learning Techniqueschine Learning Techniques
Main Article Content
Abstract
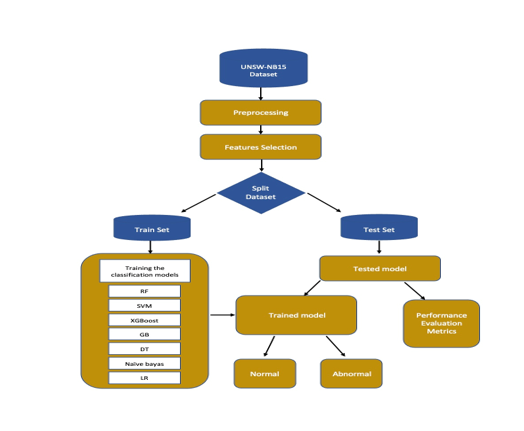
Strong cybersecurity measures are becoming vitally crucial as cloud computing utilization rises. Advanced and dynamic cyberthreats are frequently difficult for traditional intrusion detection systems (IDS), which rely on preset signatures and rules, to identify. This study improves the detection of known and unknown intrusions in cloud systems using Machine Learning (ML) methods. The UNSW-NB15 dataset was used to train and assess a num- ber of ML classifiers, including Random Forest (RF), Decision Tree (DT), XGBoost, Naïve Bayes (NB), Support Vector Machine (SVM), Logistic Regression (LR), and Gradient Boosting (GB). It uses full feature training across several classifiers and also investigates the implications of feature reduction, in contrast to many other studies that mainly employ full feature sets to train RF alone. Critical metrics including accuracy (ACC), precision, recall, and F1-score are used to analyze classifier performance and provide a thorough evaluation of their efficacy in in- trusion detection. The findings show that using all characteristics the RF and DT obtained perfect accuracy (1.00). In the case of less characteristics when using feature selection techniques (RF-based selection, information gain, or mutual information), the RF retained the best accuracy (0.94), whereas NB performed the worst overall. This study emphasizes the significance of feature selection in enhancing IDS performance and shows that ML-based techniques may greatly increase threat detection in cloud settings, even when feature dimensionality is lowered.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.