A Hybrid CNN-BLSTM Model for Phishing Attack Detection Using Deep Learning to Strengthen Internet Security
Main Article Content
Abstract
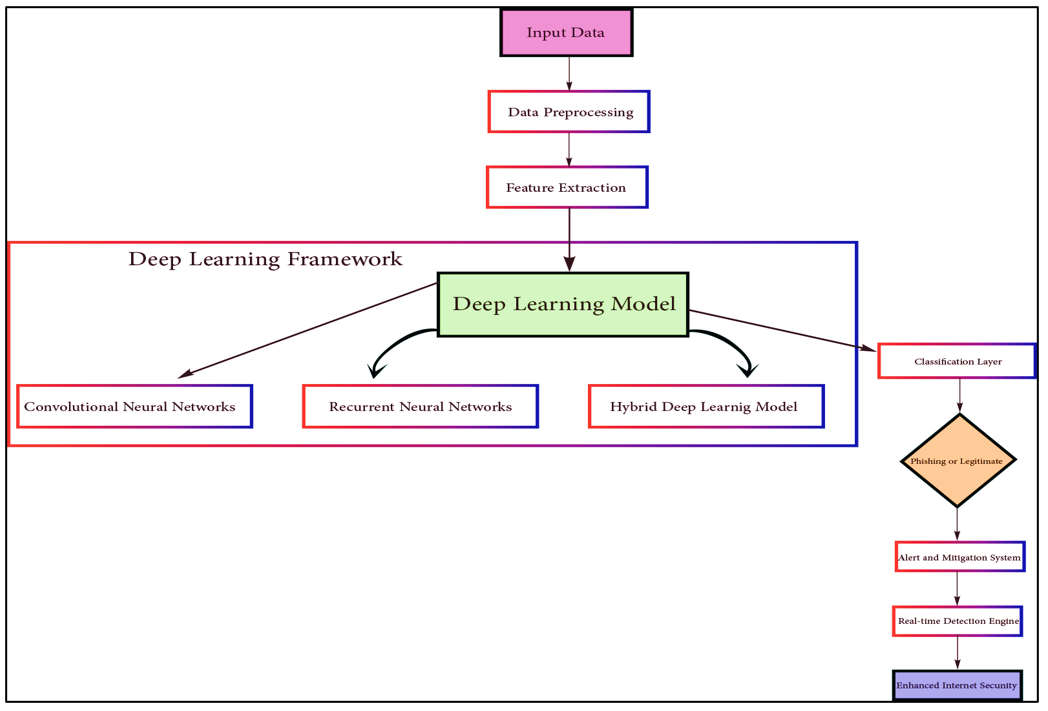
Phishing attacks continue to be a persistent and critical challenge in the cybersecurity landscape, exploiting weaknesses in Internet security through sophisticated tactics, such as social engineering, deceptive domain names, and URL obfuscation. Traditional detection systems often fail to identify these evolving threats because of their limited adaptability and high false positive rates. In this study, a deep learning approach is proposed to enhance the accuracy of phishing detection and minimize erroneous classifications. Leveraging a comprehensive dataset composed of key URL-related features, including URL structure, domain age, presence of HTTPS, and lexical patterns, we implemented and compared the performance of four deep learning models: Convolutional Neural Network with Bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory (CNN-BLSTM), Self-Normalizing Neural Network (SNN), Transformer, and Deep Belief Network (DBN). Among these, the CNN-BLSTM model achieved the highest accuracy of 81\%, demonstrating its superior ability to capture sequential and spatial patterns inherent in phishing URLs. The experimental results confirm that deep-learning methods outperform conventional techniques in detecting phishing attempts. However, challenges such as high computational complexity limit real-time deployment. This study highlights the transformative potential of deep learning for strengthening online threat detection and enhancing cybersecurity defenses.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.