Enhanced Asynchronous Advantage Actor-Critic (EA3C) Algorithm for Intrusion Detection in IIoT Environment
Main Article Content
Abstract
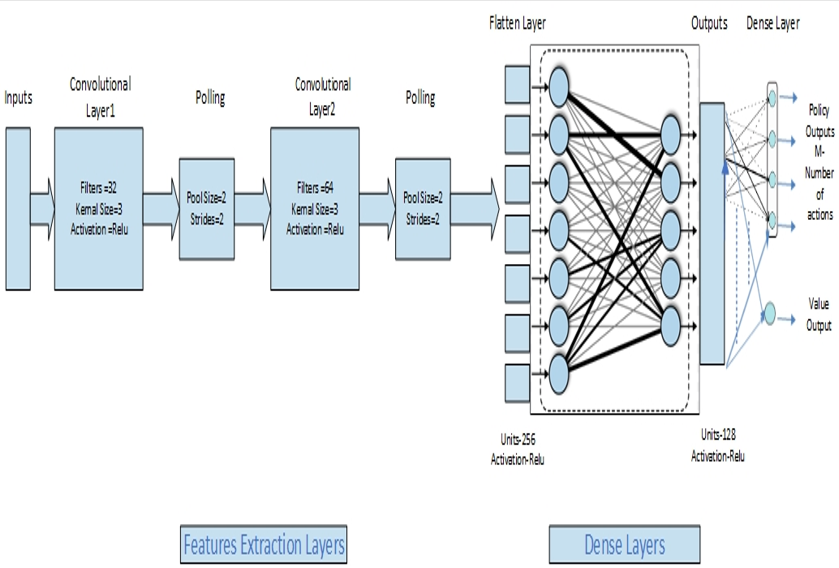
Intrusion detection is crucial for securing Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) networks, especially within edge computing environments. Traditional Intrusion Detection Systems (IDSs) struggle with the complexity and dynamic nature of IIoT networks, where increasing intrusion classes make classification tasks more challenging. While the Asynchronous Advantage Actor-Critic (A3C) algorithm has shown promise in reinforcement learning-based IDSs, previous A3C implementations suffer from slow convergence, high variance, unstable gradient updates, and inefficient parameter synchronization. These issues limit their ability to accurately classify diverse attack patterns, particularly underrepresented intrusion types. To address these challenges, this research introduces an Enhanced A3C (EA3C) using an enhanced convolutional neural network (CNN) structure to significantly improve feature representation compared to traditional fully connected networks from the dataset before passing them to the policy and value networks. Additionally, gradient clipping will be applied to prevent exploding gradients, and bootstrapping-based reward handling will be used to enhance policy and value estimation for better long-term learning and improved intrusion detection performance. The proposed approach is evaluated using the X-IIoTID dataset, which is a comprehensive benchmark that is effective in detecting a wide range of cyber threats in IIoT environments. Experimental results indicate that the EA3C algorithm significantly outperforms Decision Tree (DT), Adversarial Environment Reinforcement Learning (AERL), Double Deep Q-Network (DDQN), and traditional A3C algorithms, particularly in identifying underrepresented attack classes. The results of EA3C show that its weighted Accuracy, Precision, Recall, and F1-score exceeded 0.98, making it suitable for practical use with the increasing number of labeled classes of cyber-attacks. Although these results are promising, this algorithm needs further improvement, especially for attacks with very small samples or attacks that occur for the first time, such as zero-day attacks.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.