Microbiological Quality Assessment of Ice Cream Produced in Yemen
Main Article Content
Abstract
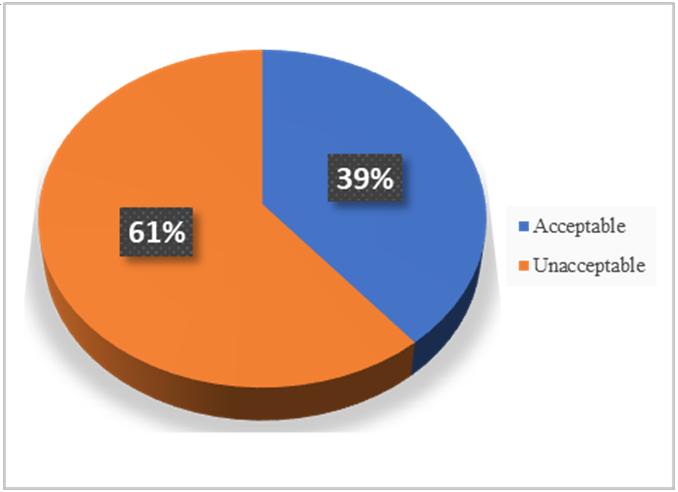
The microbiological quality of ice cream produced in Yemen was assessed to evaluate compliance with food safety standards and identify potential health risks. A total of 100 samples were collected from three Yemeni governorates (Sana’a, Ibb, and Hodeidah) and analyzed for aerobic plate count, Enterobacteriaceae, Escherichia coli, Salmonella spp., Staphylococcus aureus, mold, and yeast counts. The results showed that 61% of the samples were contaminated, failing to meet acceptable microbial quality standards. Significant disparities were observed between large and small factories, with 52% of samples from large factories meeting the standards compared to only 26% from small factories (P = 0.013). Escherichia coli contamination was detected in 28% of small factory samples, while yeast and mold contamination was significantly higher in small factories (72%) compared to large factories (36%) (P = 0.013). Packaging type also had a significant impact on microbial quality (P = 0.003), with unpackaged samples showing substantially higher contamination rates than packaged samples. No Salmonella spp. or Staphylococcus aureus was detected in any samples, reflecting effective control of these pathogens. The findings emphasize the importance of implementing stringent hygiene practices and improving microbiological monitoring, especially in small-scale production facilities, to ensure the safety and quality of ice cream in Yemen.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.