E Effect of agricultural substrates mixtures on yield and components in oyster mushroom (Pleurotus ostreatus)
Main Article Content
Abstract
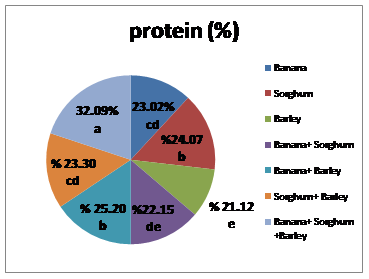
Mushroom cultivation is virtually non-existent in Yemen, despite it becoming increasingly common as an effective biotechnological practice for recycling agricultural by-products into valuable human food. Most farmers dispose of their agricultural waste, while it could be utilized beneficially as substrates for mushroom production.This study was conducted to investigate the effect of available agricultural waste mixtures on the growth of fungus Pleurotus ostreatus, yield and their components when used as substrates. Various agricultural waste and their mixtures were used, including banana, sorghum, barley, (banana + sorghum in a 1:1 ratio), (banana + barley in a 1:1 ratio) (sorghum + barley in a 1:1 ratio) and (banana + sorghum + barley in a 1:1:1 ratio), as substrates for improving fungus Pleurotus ostreatus growth. The experiment was carried out using a completely randomized design. The substrates were sterilized after preparation and packed into heat-resistant polypropylene bags. They were then inoculated with spawn and incubated. The results indicated that the shortest incubation period was observed (21.67 days) when using barley straw as a substrate. Additionally, the shortest duration for incubation and the formation of pinheads was achieved with the mixture of sorghum and barley, with durations of (25.67 and 10 days, respectively). The results showed that the highest number of clusters was obtained when using the substrate composed of a mixture of sorghum + barley, reaching 3.33 clusters. The maximum average number of fruits was recorded for the substrate mixtures when using the composed mixture of banana and barley, with a count of 7.00 fruit/cluster. Furthermore, the highest total productivity was obtained from the substrate composed of a mixture of (sorghum + barley), amounting to (810 g) with a biological efficiency of 91.2%. The fruiting bodies were analyzed for protein content, and the highest protein percentage (32.09%) was recorded when using the substrate mixture of (banana + sorghum + barley). Based on the research findings, we can conclude that agricultural waste mixtures can lead to increased productivity of oyster mushrooms and utilize the abundance of agricultural waste for mushroom production, enhancing their properties by incorporating them with barley residues. This, in turn, provides an alternative protein source.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.