Enabling Arabic Database Querying via Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models
Main Article Content
Abstract
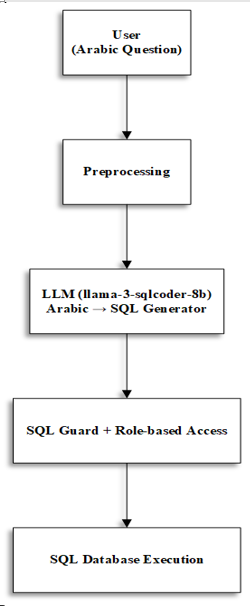
Recent advancements in Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Text-to-SQL systems have enabled easier interaction with relational databases. However, most solutions focus on English, leaving Arabic underrepresented. This study addresses that gap by fine-tuning the Llama-3-SQLCoder model to convert Arabic text into correct and executable SQL, enabling non-technical users to work with databases without learning SQL syntax. We enhanced the model using Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) and Unsloth, training it on Arabic questions paired with SQL queries from the Northwind database. To support low-resource environments, the model was converted to the GGUF format, reducing computational requirements while preserving performance. Evaluation results showed an execution accuracy of 90.24% and a validity rate of 97.56%, outperforming the zero-shot baseline (44% and 80%). The model also achieved an Exact Match score of 32% and an F1 score of 0.83, compared to 12% and 0.61 for the baseline. These findings demonstrate that LoRA and Unsloth are effective for adapting SQL-specialized models to Arabic. Despite these improvements, the system still struggles with complex nested queries and dialectal variations, indicating areas for future work. Overall, this study contributes to narrowing the gap between Arabic and other languages in Text-to-SQL research and improves database accessibility for non-technical users.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
References
Rayhan, et al., "Natural Language Processing:
Transforming How Machines Understand
Human Language.," Conference: The
development of Artificial General Intelligence,
D. Gao et al., “Text-to-SQL Empowered by
Large Language Models: A Benchmark
Evaluation,” Proc. VLDB Endow., vol. 17, no. 5,
pp. 1132–1145, Jan. 2024,doi:
14778/3641204.3641221.
X. Zhu, Q. Li, L. Cui, and Y. Liu, “Large
Language Model Enhanced Text-to-SQL
Generation: A Survey,” Oct. 08, 2024. doi:
48550/arxiv.2410.06011.
S. Almohaimeed, S. Almohaimeed, M. Ghanim,
and L. Wang, “Ar-Spider: Text-to-SQL in
Arabic,” Feb. 22, 2024. doi:
48550/arxiv.2402.15012.
Z. Hong et al., “Next-Generation Database
Interfaces: A Survey of LLM-based Text-toSQL,” June 12, 2024. doi:
48550/arxiv.2406.08426.
P. Shi et al., “Cross-lingual Text-to-SQL
Semantic Parsing with Representation Mixup,”
Association for Computational Linguistics, Jan.
, pp. 5296–5306. doi:
18653/v1/2022.findings-emnlp.388.
S. Chafik, S. Ezzini, and I. Berrada,
“Dialect2SQL: A Novel Text-to-SQL Dataset for
Arabic Dialects with a Focus on Moroccan
Darija,” Jan. 20, 2025. doi:
48550/arxiv.2501.11498.
Aswin Ak, "Defog AI Introduces LLama-3-
based SQLCoder-8B: A State-of-the-Art AI
Model for Generating SQL Queries from Natural
Language,"
https://www.marktechpost.com/2024/05/15/defo
g-ai-introduces-llama-3-based-sqlcoder-8b-astate-of-the-art-ai-model-for-generating-sqlqueries-from-natural-language/, 2024.
A. Agrahari, A. Gautam, P. K. Ojha, and P.
Singh, “SFT For Improved Text-to-SQL
Translation,” Feb. 13, 2024, Mdpi Ag. doi:
20944/preprints202402.0693.v1.
E. Hu et al., “LoRA: Low-Rank Adaptation of
Large Language Models,” June 17, 2021. doi:
48550/arxiv.2106.09685.
Unsloth.ai, "Fine-tuning LLMs guide," 2025.
[Online]. Available: https://docs.unsloth.ai/getstarted/fine-tuning-llms-guide.
T. Shi, K. Tatwawadi, K. Chakrabarti, Y. Mao,
O. Polozov, and W. Chen, “IncSQL: Training
Incremental Text-to-SQL Parsers with NonDeterministic Oracles,” Sept. 13, 2018. doi:
48550/arxiv.1809.05054.
V. Zhong, C. Xiong, and R. Socher, “Seq2SQL:
Generating Structured Queries from Natural
Language using Reinforcement Learning,” Aug.
, 2017. doi: 10.48550/arxiv.1709.00103.
T. Yu et al., “Spider: A Large-Scale HumanLabeled Dataset for Complex and Cross-Domain
Semantic Parsing and Text-to-SQL Task,”
Association for Computational Linguistics, Jan.
doi: 10.18653/v1/d18-1425.
M. Shah, "Transforming Natural Language Text
to SQL: Harnessing RAG and LLMs for
Precision Querying," medium, 2024.
A. Vaswani et al., “Attention Is All You Need,”
June 12, 2017. doi: 10.48550/arxiv.1706.03762.
L. Xue et al., “mT5: A massively multilingual
pre-trained text-to-text transformer,” Oct. 22,
, Cornell University. doi:
48550/arxiv.2010.11934.
E. Manjavacas et al., “BLOOM: A 176BParameter Open-Access Multilingual Language
Model,” Nov. 09, 2022, Cornell University. doi:
48550/arxiv.2211.05100.
N. Wretblad, F. Riseby, R. Biswas, A. Ahmadi,
and O. Holmström, “Understanding the Effects
of Noise in Text-to-SQL: An Examination of the
BIRD-Bench Benchmark,” Feb. 19, 2024. doi:
48550/arxiv.2402.12243.
AI@Meta, "Introducing Meta Llama 3: The
most capable openly available LLM to date,"
[Online]. Available:
https://ai.meta.com/blog/meta-llama-3/.
Hugging Face, "GGUF," GGUF, [Online].
Available:
https://huggingface.co/docs/transformers/gguf.
J. Lee et al., “Emergent Abilities of Large
Language Models,” June 15, 2022, Cornell
University. doi: 10.48550/arxiv.2206.07682.
HuggingFace, "PEFT Documentation.,"
[Online]. Available:
https://huggingface.co/docs/peft/en/index.
a. a. tatsu, "stanford_alpaca," 2023. [Online].
Available: https://github.com/tatsulab/stanford_alpaca.
W. Antoun, F. Baly, and H. Hajj, “AraBERT:
Transformer-based Model for Arabic LanguageUnderstanding,” Feb. 28, 2020. doi:
48550/arxiv.2003.00104.
T. Dettmers, S. Shleifer, M. Lewis, and L.
Zettlemoyer, “8-bit Optimizers via Block-wise
Quantization,” Oct. 06, 2021, Cornell
University. doi: 10.48550/arxiv.2110.02861.
T. Brown et al., “Language Models are FewShot Learners,” May 28, 2020, Cornell
University. doi: 10.48550/arxiv.2005.14165.
X. Xu, C. Liu, and D. Song, “SQLNet:
Generating Structured Queries From Natural
Language Without Reinforcement Learning,”
Nov. 13, 2017. doi: 10.48550/arxiv.1711.04436.
Y. Huang et al., “Exploring the Landscape of
Text-to-SQL with Large Language Models:
Progresses, Challenges and Opportunities,” May
, 2025. doi: 10.48550/arxiv.2505.23838.