Suitability Analysis of Solar Energy Plant Sites in Yemen Using AHP, BWM, and GIS Methods
Main Article Content
Abstract
The study presents a comprehensive evaluation of optimal locations for solar energy facilities in Yemen by com-
bining Geographic Information System (GIS) technology with Multi-Criteria Decision-Making (MCDM) methodolo-
gies. It identifies twelve crucial criteria, assigning weights through the Analytical Hierarchy Process (AHP) and
subsequently validating them using the Best-Worst Method (BWM). A weighted overlay analysis conducted in
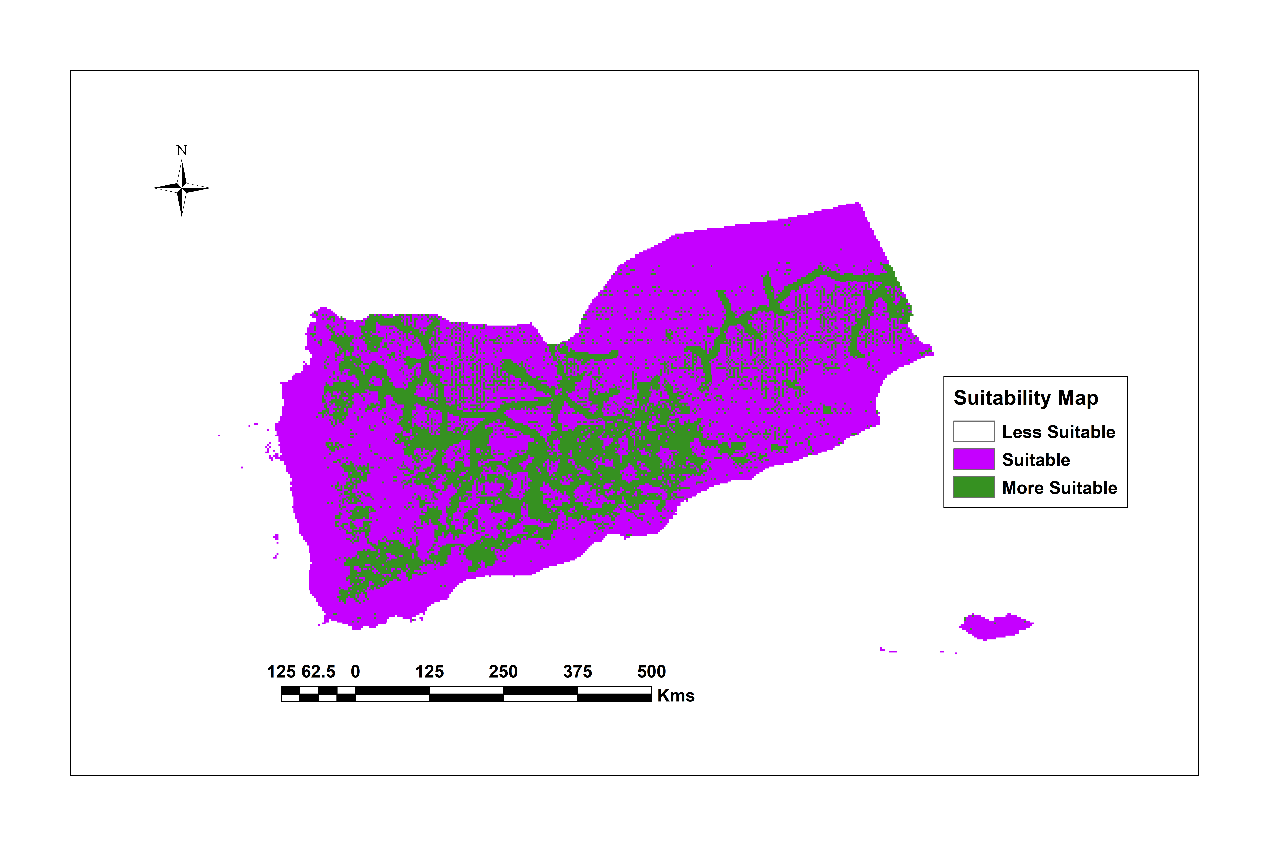
GIS resulted in a national suitability map, indicating that the eastern, southern, and northern regions of Yemen are
particularly well-suited for solar energy development. The findings reveal that 30.84% of the country is classified
as highly suitable, while 69.16% is moderately suitable, and merely 0.0022% is deemed less suitable for solar
installations. The sensitivity analysis highlights the significant influence of weighting the criteria, as even slight modifications to factors such as Global Horizontal Irradiance (GHI) and slope can lead to substantial changes in suitability assessments. Overall, the integration of AHP, BWM, and GIS is shown to create a robust framework for solar site selection, providing practical guidance for policymakers and energy planners in Yemen.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.