Prevalence of Infectious Markers among Blood Donors in Sana’a, Yemen: A Cross-Sectional Study
Main Article Content
Abstract
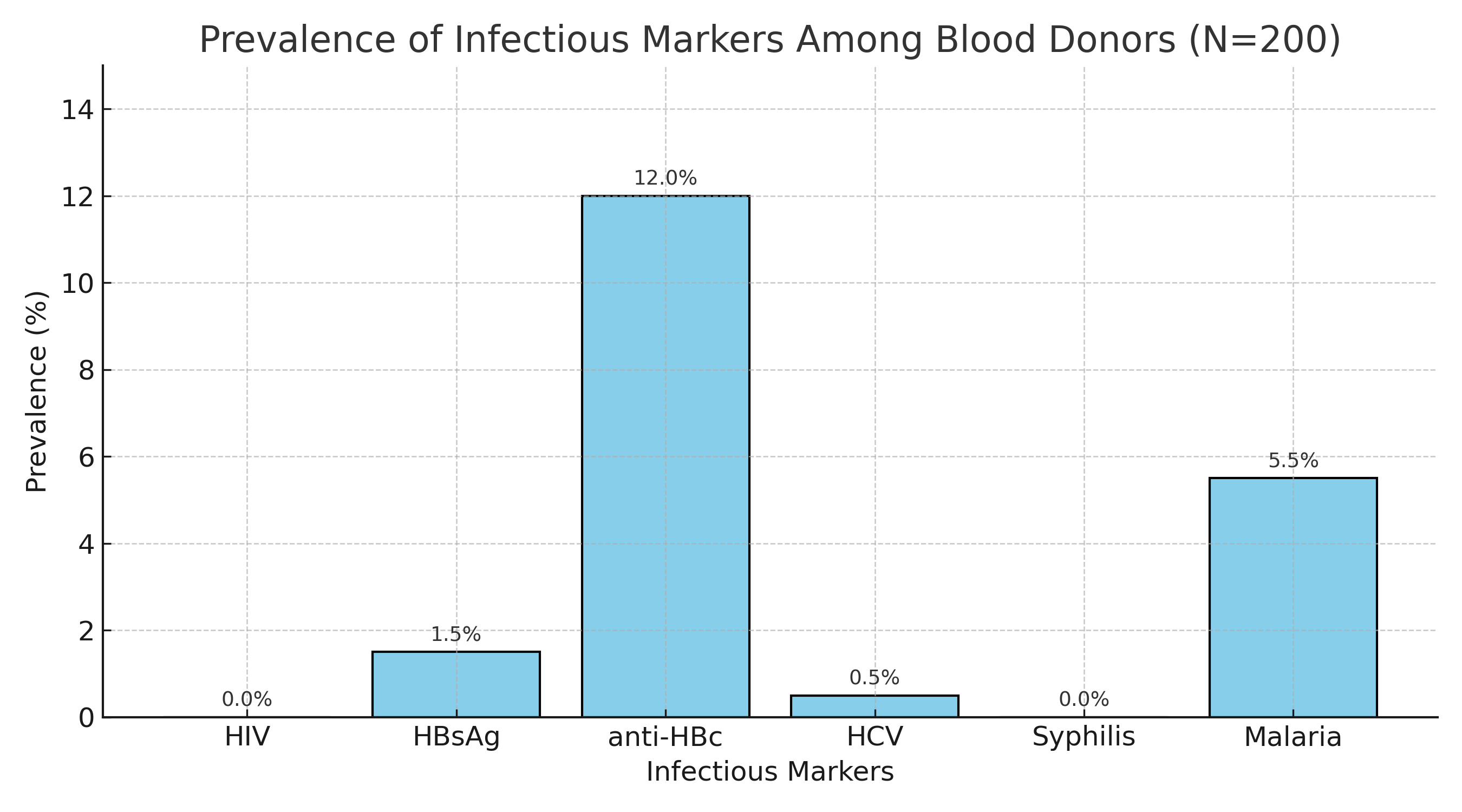
Blood transfusion is a vital therapeutic procedure but carries the risk of transfusion-transmissible infections, particularly in resource limited settings. This cross-sectional study was conducted to determine the prevalence of infectious markers among voluntary male blood donors in Sana’a, Yemen, Brazil. A total of 200 donors aged 18–60 years were recruited between June 2024 and May 2025 from three major facilities: Al-Kuwait University Hospital, National Blood Transfusion and Research Center, and National Center for Central Public Health Labora-tories in Sana’a City, Yemen. Blood samples were screened for HIV, HBsAg, anti-HBc, HCV, syphilis (Treponema pallidum), and malaria using ELISA and microscopy. Overall, 25 donors (12.5%; 95% CI: 8.6–17.8) were positive for at least one infectious marker. Anti-HBc was the most common (7.0%), followed by malaria (5.5%), while HBsAg and HCV were less frequent (1.5% and 0.5%, respectively), and no cases of HIV or syphilis were detected. Statistical analysis showed significant associations between HCV and shamma use (p = 0.017) and between anti-HBc and educational level (p = 0.006), whereas smoking demonstrated a borderline association with anti-HBc (p = 0.057). No significant relationships were found between malaria or HBsAg and sociodemographic or behavioral variables. The results indicate that exposure to hepatitis B virus and malaria remains the predominant transfusion-related risk in this population, whereas exposure to HIV and syphilis appears negligible. These findings underscore the importance of strengthening donor education, sustaining HBV vaccination and screening programs, and improving malaria prevention strategies to enhance the safety of blood transfusion in Yemen
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.