Structural, Optical and Cytotoxic Analysis of Sr-Doped CuS Nanoparticles for Lung Cancer Applications
Main Article Content
Abstract
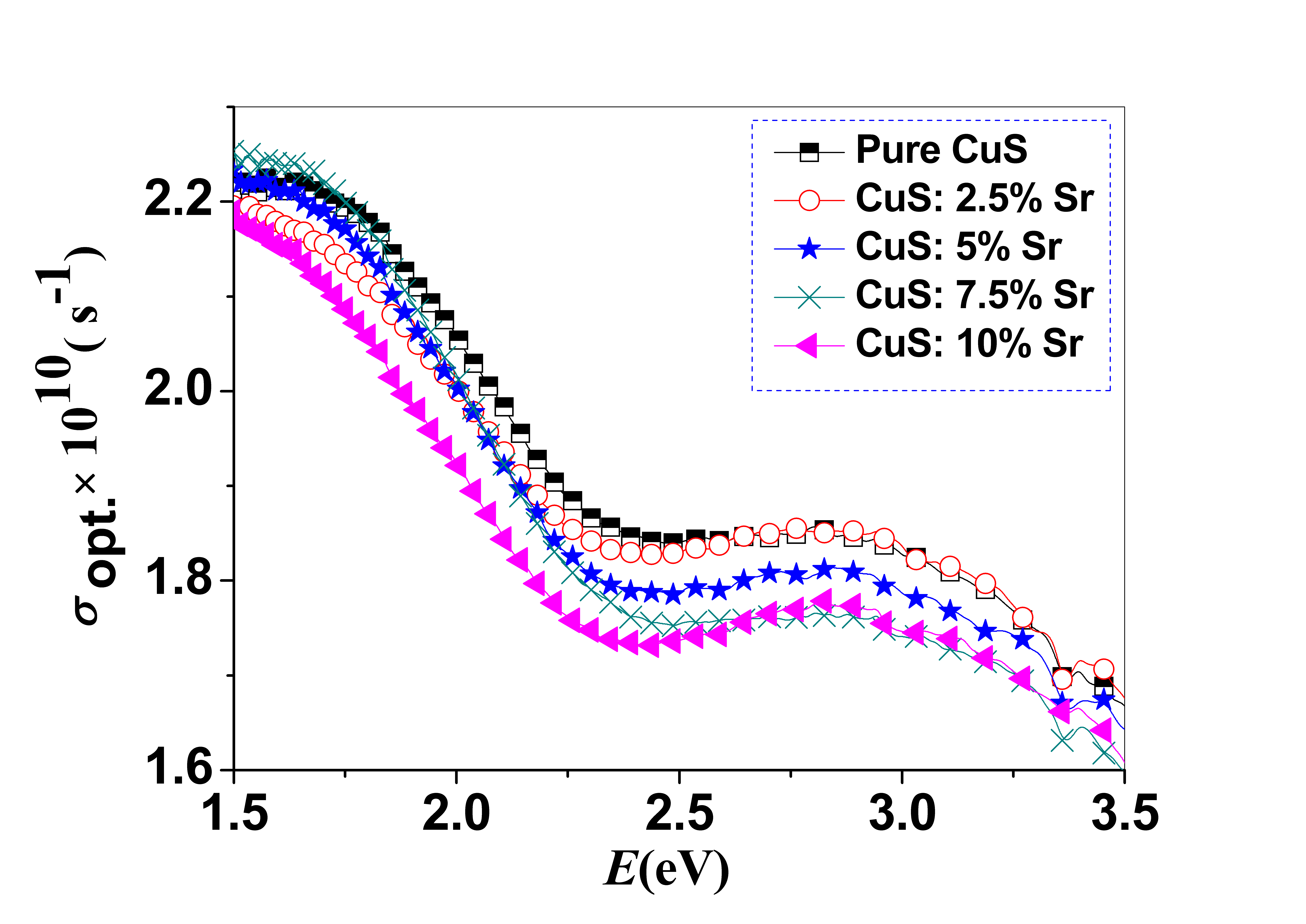
Copper sulfide (CuS) nanoparticles have garnered significant interest due to their unique structural, optical, and biological properties, making them promising candidates for cancer therapy. This work systematically examines how strontium incorporation influences the structural properties, optical behavior, and anticancer activity of copper sulfide nanoparticles for potential lung cancer therapeutics. Using the co-precipitation approach, Sr-doped CuS nanoparticles with different Sr concentrations were produced. Characterization techniques, including XRD, TEM, and UV-VIS-NIR spectroscopy, were employed to analyze their physicochemical properties. The results indicate that Sr doping enhances crystallinity, modifies the bandgap, and influences optical conductivity. Cytotoxicity analysis using MTT assays on A549 lung cancer cells emonstrated that Sr-doped CuS nanoparticles exhibit enhanced anticancer activity compared to pure CuS. The 2.5% Sr-doped sample showed the most significant reduction in cell viability. These findings suggest that Sr-doped CuS nanoparticles are promising candidates for biomedical applications. However, further studies are needed to assess their photothermal and photodynamic effects under controlled light exposure.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.