the Characterization, Antibacterial and Antioxidant of Phytosynthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Aloe Fleurentinorum Leaves Extract
Main Article Content
Abstract
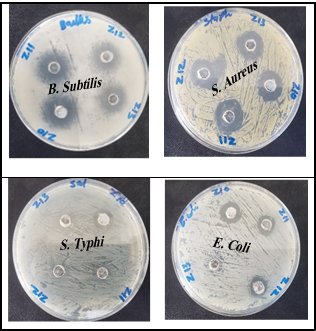
The environmentally friendly methods for synthesizing metal oxide nanoparticles effectively save time, money, and effort. These methods involve the phytosynthesis process, which depends on plant extracts. To produce zinc oxide nanoparticles (ZnO − NPs), we used at this work an extract of Aloe Fleurentinorum Leaves (AFL) as a reducing, capping, and stabilizing agent. As well as the effect of altering some parameters on the synthesis of ZnO − NPs, such as the Temperature (T), the potential of hydrogen (pH), and the volume ratio (V/V), was studied using an X-ray diffractometer (XRD), crystallite size, and microstrain was determined, and the average crystallite size was between 16.50, and 25.99 nm. Also, ZnO − NPs were characterized optically by a UV-Vis spectrophotometer and got 3.13 eV band gap energy. Fourier transfer infrared spectroscopy was used for characterization. The antibacterial activities of ZnO − NPs were investigated against four bacterial species, and the results exhibit a noticeable effect, especially against gram-positive species, with inhibition zones ranging from 17 to 20 mm for the different concentrations. Also, the DPPH free radical method was used to evaluate the antioxidant properties of the synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles at various concentrations, which showed a moderate scavenging efficiency of 52.74% at 800 µg/mL.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.