Risk factors, microbiological etiology, and clinical manifestations of UTIs in patients presenting to urology clinics in major hospitals in Sana’a City, Yemen
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background and aims: Urinary tract infections (UTIs) remain largely under-researched despite their common occurrence in clinical practice. This study focuses on outpatient urology clinic visits in Sana’a City, aiming to assess the prevalence of clinical symptoms, bacterial characteristics, and risk factors associated with both bacterial and fungal UTIs.
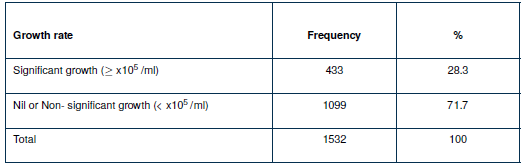
Methods: In a 12-month cross-sectional study involving 1532 patients suspected of having a urinary tract infection (UTI), 433 culture-positive samples were identified. Urine samples were collected along with clinical and demographic data through a standard questionnaire. Laboratory procedures were employed to isolate, cultivate, and identify potential bacterial pathogens, while also examining risk factors associated with UTIs.
Results: The majority of patients were aged 21–30 years (25.6%), and the most common symptoms were urine turbidity (85.1%), urinary urgency (78.0%), fever (64.7%), and dysuria (52.3%), while hematuria, kidney pain, and nausea/vomiting were less frequent. Escherichia coli (41.3%), Pseudomonas aeruginosa (18.5%), Klebsiella pneumoniae (9.1%), S.aureus (9.7%), Proteus mirabilis (1.7%), Acintobacter lowfii (0.46%), and Citrobacter freundii (1.2%) were the Gram-negative isolates. Staphylococcus haemolyticus (1.7%), Staphylococcus saprophyticus (5.8%), and Enterococcus faecalis (5.5%) were the Gram-positive isolates. Additionally, 5.3% of the isolates were of the Candida species. There were significant risk factors for contracting UTI, including diabetic mellitus (OR = 4.9), renal disorders (OR = 2.8), autoimmune diseases (OR = 3.3), khat chewing (OR = 1.7), catheterization (OR = 3.6), stones (OR = 2.9), immunosuppressive medications (OR = 2.8), hypertension (OR = 6.5), previous urinary tract infection (OR = 7.8), active sexual intercourse (OR = 5.2), familial urinary tract infection (OR = 3.8), depression and psychosis (OR = 4.1), and obesity (OR = 2.5), all of which had significant 2 and p-values.
Conclusions: The most common isolates of UTI was Escherichia coli. The results show the most common symptoms of UTI are urine turbidity, urinary urgency, fever and dysuria. There were significant risk factors for UTIs, including all known risk factors for UTIs except kidney transplants.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.