Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction and HPLC Quantitative Profiling of Phytochemical Compounds in Yemeni Red Onion Peels (Allium cepa L.)
Main Article Content
Abstract
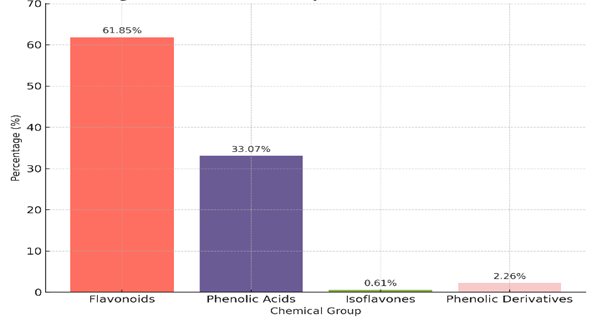
This study reports the ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE) and quantitative profiling of antioxidants in methanolic extracts of Yemeni red onion peels (Allium cepa L.) using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The HPLC profiling identified a chemically diverse composition comprising 15 Phenolic compounds classified into four major groups: Flavonoids (61.85 %), Phenolic Acids (33.07 %), Isoflavones (0.61 %), and Phenolic Derivatives (2.26 %). Quercetin was the predominant compound with a concentration of 52289.14 μg/g DW, followed by Chlorogenic acid 18,761.89 μg/g DW, alongside significant amounts of Gallic acid, Ellagic acid, and Daidzein. The results indicate a high Phenolic content and strong antioxidant potential in Yemeni red onion peels, confirming their suitability as a natural source of bioactive compounds for nutraceutical and pharmaceutical applications.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
Funding data
-
Nanoscience and Nanotechnology Area of Advance, Chalmers Tekniska Högskola
Grant numbers none