The relationship between helicobacter pylori infection and iron deficiency anemia in Yemeni adults
محتوى المقالة الرئيسي
الملخص
Abstract
Background: Iron deficiency anemia (IDA) represents a common nutritional and hematological disorder. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), primarily recognized for its role in gastritis, peptic ulcers, and gastric cancer, has recently demonstrated a notable correlation with IDA according to emerging research. This study aims to evaluate the potential relationship between H. pylori infection and the development of IDA.
Materials and Methods: This case-control study included 100 participants between the ages of 18-56. The study group consisted of 50 individuals with confirmed H. pylori infection, while the control group comprised 50 healthy subjects. We conducted analyses of stool specimens for H. pylori antigens and occult blood. Additionally, we collected blood samples to evaluate complete blood counts and iron profiles using standardized automated systems.
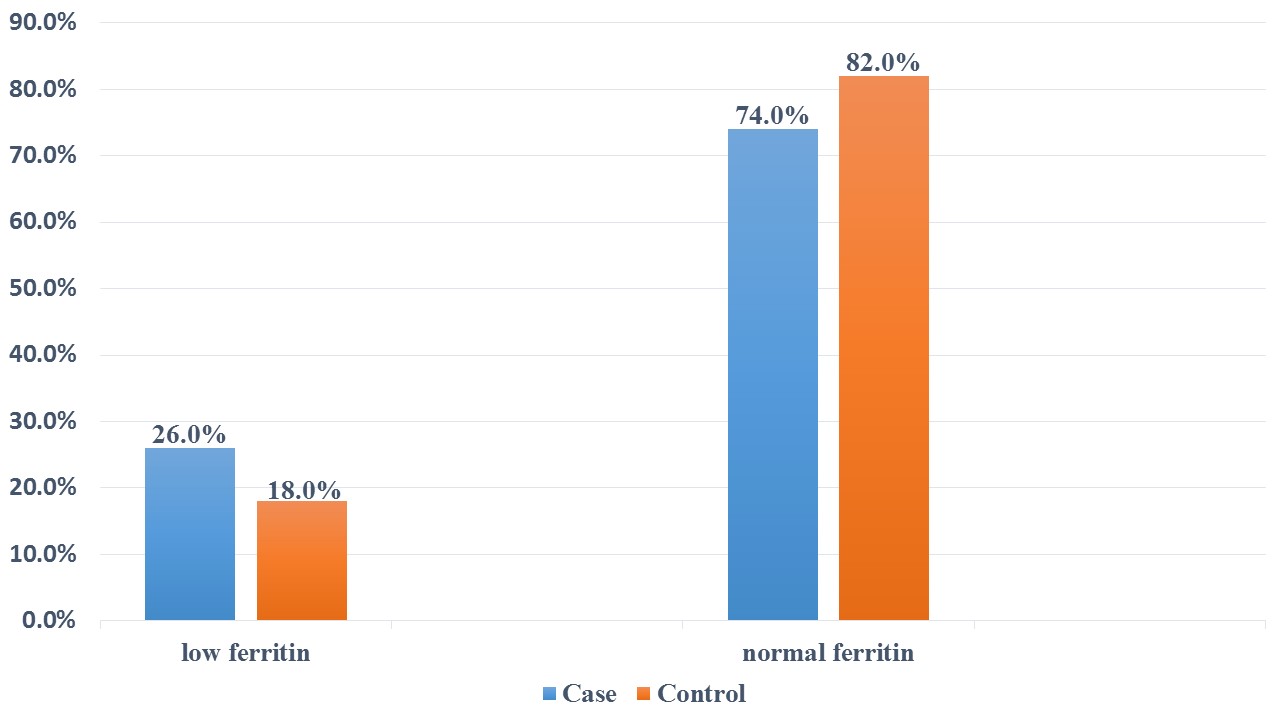
Results: Our analysis revealed no statistically significant variations in demographic characteristics or risk factors between the study and control groups. The majority of participants (90% of the patient group and 92% of controls) presented without anemia. Low ferritin levels were observed in 26% of the patient group and 18% of the control group. We did not identify significant differences in hematological parameters, serum iron, or ferritin concentrations between H. pylori-positive individuals and controls. Furthermore, total iron-binding capacity (TIBC) and unsaturated iron-binding capacity (UIBC) values showed no significant elevation in the study group compared to controls.
Conclusion: H. pylori infection does not demonstrate a significant association with iron deficiency anemia. Key indicators including hemoglobin levels, serum iron, ferritin, TIBC, and UIBC remained statistically comparable between H. pylori-infected participants and healthy controls.
التنزيلات
تفاصيل المقالة

هذا العمل مرخص بموجب Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.