Comparative Analysis of Lateral Incisor Morphology in Patients with Unilateral Palatally Impacted Canines: A CBCT Study
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background and objectives:
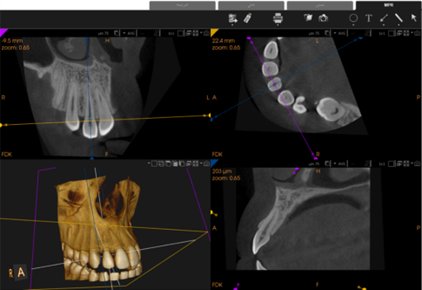
This study aimed to evaluate the morphology of maxillary lateral incisors in patients with unilateral palatally impacted canines compared to the contralateral side using cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) technique.
Materials and Methods:
A cross-sectional study analyzed CBCT images of 70 patients (35 males and 35 females; mean age, 25.83 ± 9.27 years) with unilateral palatally impacted canines. The lateral incisor length, crown width, and colum angle were evaluated on both the impacted and non-impacted sides. Paired and independent t-tests were used for comparisons, and intraclass correlation coefficients (ICCs) were used to assess intra- and inter-examiner reliability. Statistical significance was set at P < 0.05.
Results:
The results revealed a statistically significant difference in lateral incisor length between the impacted side (21.81 ± 2.28 mm) and the non-impacted side (22.12 ± 2.03 mm). In contrast, crown width and collum angle did not show any significant differences. In the gender-based comparison, the lateral incisor length was significantly reduced in female participants (p = 0.006). All ICC values indicated excellent agreement (ICC > 0.9).
Conclusion:
The lateral incisor was significantly shorter on the impacted side than on the non-impacted side, supporting its potential role as a clinical predictor of palatal canine impaction. In contrast, there were no significant differences in the crown width or colum angle of the lateral incisors.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.