Acute Myeloid Leukemia among Patients attending Sana’a Hospitals, Yemen: Prevalence, Subtypes and Hematological Patterns
Main Article Content
Abstract
Objectives: Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is malignant disorder of cells of myeloid lineage in the bone marrow due to chromosomal abnormalities, leading to accumulation of myeloblasts in the bone marrow and infiltration to peripheral tissues. The aim of this study was to determine the prevalence, subtypes and hematological patterns of AML among patients attending Sana’a hospitals, Yemen.
Materials and methods: This cross-sectional study was carried out on total 257 patients with hematological malignancies (HMs) during the period from November 1, 2023 to March 31, 2024. Among HMs, there were 79 patients diagnosed with AML by complete blood count (CBC), by Giemsa stained blood/BM films, and by immunophenotyping using flow cytometry. Data was analyzed using SPSS-26.
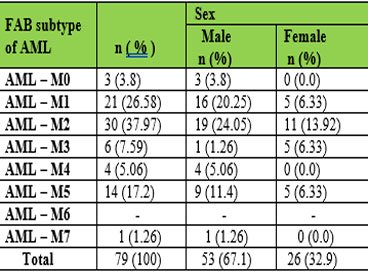
Results: Among 257 patients with HMs, AML was found in 79 patients with prevalence of 30.7%. AML patients included 53 (67.1%) males and 26 (32.9%) females., with M:F ratio of 2:1 and aged between 4 and 80 years, FAB-M2 was the most common subtype of AML in 30 (37.97%) of patients; among them, there were 19 (24.05%) males and 11 (13.92%) females, the M:F ratio is 1.7:1. FAB-M2 was followed by M1 (26.58), M5 (17.2), M3 (7.59), M4 (5.06), M0 (3.8) and M7 (1.26). The hematological patterns included decreased Hb, increased WBC and decreased platelets in 97.5%, 82.3% and 96.2% of patients, respectively.
Conclusion: Leukemia was the most prevalent type among hematological malignancies. The prevalence of AML was high and represent the second leukemia type. AML-M2 was the common subtype of AML.
Downloads
Article Details

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.